

Zeaxanthin
Other Research Topics
Zeaxanthin is a geometrical isomer of Lutein. It is available in 3 forms, Trans- Zeaxanthin [3R-3Rí], Meso-Zeaxanthin [3R-3Sí] and [3S-3Sí]. The Trans- zeaxanthin is also known as
β-β-carotene-3R-3Rí diol. This is a natural form of Zeaxanthin and very closely associated with Lutein in Marigold flowers.
Importance of Zeaxanthin
In vitro evidence suggests that zeaxanthin's extra conjugated double bond may make it a better antioxidant than Lutein. The effect would be synergic when taken in combination
Recommended daily intake
While no recommended daily allowance currently exists for Zeaxanthin as for other nutrients, 2-4mg in Dietary supplementation may help prevent AMD. The combination of 5mg of Lutein and 1 mg of Zeaxanthin is the one found in AREDS 2 composition.
The Meso-Zeaxanthin is also known as b-b-carotene-3R-3Sí diol. This is obtained by catalytic isomerisation process from Lutein and hence is a semi-synthetic molecule.
In vitro evidence suggests that zeaxanthin's extra conjugated double bond may make it a better antioxidant than Lutein. The effect would be synergic when taken in combination
Recommended daily intake
While no recommended daily allowance currently exists for Zeaxanthin as for other nutrients, 2-4mg in Dietary supplementation may help prevent AMD. The combination of 5mg of Lutein and 1 mg of Zeaxanthin is the one found in AREDS 2 composition.
The Meso-Zeaxanthin is also known as b-b-carotene-3R-3Sí diol. This is obtained by catalytic isomerisation process from Lutein and hence is a semi-synthetic molecule.
About Us
With over 5000 contract farms, a Worldclass cGMP Compliant Manufacturing Facility in Attibele and dedicated Oleoresin Manufacturing Plants, we have complete control over the entire value chain.

Lutein Ester: Lutein Esters is a form of Lutein having one or more fatty acid chain attached through the end hydroxyl groups of free Lutein.
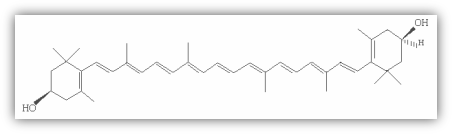
The other form is the
β-β-carotene-3S-3Sí diol.
Lutein: Lutein is chemically hydrolyzed form of Lutein Esters. They are also naturally available in the free form especially in corn. In Marigold it is predominantly available with Zeaxanthin. It is mostly available in Trans form. The other form is cis form which is available in traces.







